Key Benefits of Implementing RPA
Every industry is burdened by processes that are repetitive, tedious, time-consuming, and expensive. What if there was a way to reduce the cost, increase efficiency, and improve the deliverability of the results of these processes?
Many businesses are discovering that Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is the solution that does just that. So, what is robotic process automation, and how can it improve your company’s performance?
What is Robotic Process Automation?
Robotic process automation (also referred to as RPA) is the application of technology to reduce the necessity for human labor. RPA solutions seek to automate menial, repetitive tasks and move the burden of those tasks away from people and onto machines.
Robotic process automation encompasses everything from creating an automated email response when you are away from work to deploying thousands of artificially intelligent bots to track and manage investment trading.
Benefits of Robotic Process Automation
The primary benefit of RPA is that it frees human capital to engage in high-level thinking and creativity rather than spending many hours engaged in repetitive, low-benefit tasks. Robotic process automation also decreases overhead, as humans are more expensive to employ than robots.
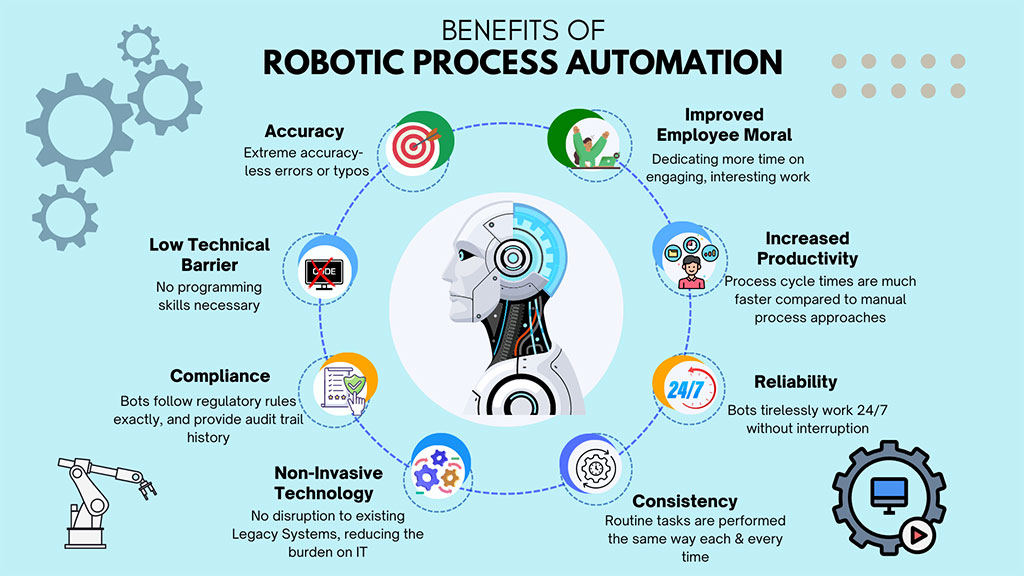
Robots are also better at doing these types of menial tasks than humans. They are faster and more accurate. Properly configured, software robots can increase a team’s productivity by up to 50%, with fewer errors and lower costs.
Types of Robotic Process Automation
The three major types of robotic process automation are attended automation, unattended automation, and hybrid RPA.

Attended Automation
This form of RPA is triggered by the user and typically replaces part of the process that a user would normally do manually. For example, if a user frequently must go through several steps in an interface to complete a task, they could instead launch an attended automation RPA sequence at the moment that the series of steps begin.
Unattended Automation
Unattended automation requires no input from a user and can be deployed in batches to a cloud or other system. A good example of unattended automation is an online onboarding sequence that is automatically sent to all incoming new employees. Other examples include automated trading and finance management and processing invoices.
Hybrid RPA
Hybrid RPA employs aspects of both attended and unattended RPA. In this way, both front and back-office tasks can be automated, allowing for end-to-end automation of an entire system.
Robotic Process Automation Tools
RPA tools and solutions are sometimes presented as “workflow management” or “work process management” tools. Other names for RPA solutions include “business process automation” and “business process management.”

Today, the RPA marketplace contains a mix of both purpose-built RPA tools and older work management tools that have been updated to provide robotic process automation solutions. Some of the top RPA tools available today are those built by Appian, Automation Anywhere, Blue Prism, and UIPath.
Real-World Use Cases for RPA
RPA can be used in many applications to solve many business problems. First and foremost, simple automated workflows can increase employee productivity and efficiency on a daily basis by automating away time-consuming, repetitive tasks. Examples of this include automated customer service responses, email marketing campaigns, and data entry.
Beyond that, artificially intelligent RPA can be applied to complicated analysis needs to improve accuracy and efficiency.
Industries Using RPA Successfully.
In the beginning, robotic process automation was used in Banking, Insurance, Retail, Manufacturing, Healthcare, and Telecommunications. Now RPA is successfully used in many industries where there are many repetitive tasks to be completed and data to be entered.
- Healthcare: In the healthcare industry, it helps with appointments, patient data entry, processing claims, billing, etc.
- Retail: For the retail industry, it helps with updating orders, sending notifications, shipping products, tracking shipments, etc.
- Telecommunications: For the telecommunications industry, it helps in monitoring, fraud data management, and updating customer data.
- Banking: The banking industry uses RPA to drive increased workflows and efficiency, improved data accuracy, and improved security of data.
- Insurance: Insurance companies use RPA to manage work processes, enter customers’ data, and for applications.
- Manufacturing: For manufacturing, RPA tools help improve supply chain procedures. It also helps with the billing of materials, Administration, Customer services & support, Reporting, Data migration, etc.



































